Topics
We organise our actions in six thematic & strategic agendas:
Strategic Agendas:
Bio-economy
Circular Construction
Chemicals/Plastics
Manufacturing Industry
Food Chain
Water Cycles
Seven leverages provide additional support:
Leverage effects:
Lever Policy Instruments
Lever Circular Procurement
Lever Communication
Lever Innovation & Entrepreneurship
Lever Financing
Lever Jobs & Skills
Lever Research
What, why and how?
Why are we pursuing a circular economy?
Future visions 2050
How do we see our circular future?
About our management
Who steers what at Flanders Circular?
Overview: How To Build a Circular City Governance?
The roll-out of a circular economy requires a total systemic change and a new form of governance. A new method of collaborating – both between the city’s various departments and its inhabitants and companies – is required in order to establish an effective circular strategy.
The overview below focusses on the various roles of the city. For example, circular economy initiatives can bring benefit at the same time from both a poverty prevention perspective and a job creation viewpoint. It also demonstrates specific actions a city can take regarding its own administration or how it can stimulate and support its residents or businesses.
The overview and infographic are designed based on interviews with European frontrunners.
.png)
What can a local authority do?
Reorganise Your City
![]() Create common long term ambition, with political support & use it in your branding
Create common long term ambition, with political support & use it in your branding
Create a circular strategy if possible, but, it can also be equally effective to integrate circular principles and actions in an existing long-term climate strategy, or in a LT plan to reach the Sustainable Development Goals. Several examples of a circular vision can be found at #CEStakeholderEU.
![]() Set up cooperation between city departmants and appoint a coordinator
Set up cooperation between city departmants and appoint a coordinator
A new method of collaborating – both between the city's various departments and its inhabitants and companies – is required to effectively implement a circular strategy. Through the infographic you can see how different functions in a city can lead to circular breakthroughs, e.g. sharing initiatives have a positive impact, both from a poverty prevention perspective and from an environmental department.
![]() Act circular (circular procurement, futureproof urban planning, sustainable building,...)
Act circular (circular procurement, futureproof urban planning, sustainable building,...)
In their exemplary role, cities can have a huge impact on the implementation of a circular strategy. By using their purchasing power, they are able to grow the market for circular suppliers as well as lead by example. You can find some examples and context through The Urban Agenda on Public Procurement and the European ProCirc project with focuse on circular procurement. The Urban Agenda Circular Economy Partnership and onLand Use Partnership created a handbook together on the reuse of buildings and spaces.
![]() Get insights in your resources (waste, water, materials,...)
Get insights in your resources (waste, water, materials,...)
The lack of data and indicators for CE transition on a city level is an important barrier. Therefore, the Urban Agenda has listed 30 indicators to help cities with their strategy and in their use of data of resources for policy improvements. Collected data often end up in a drawer, but could be used as an input for circular actions.
Stimulate Citizens Initiatives
![]() Promote sharing & functional economy
Promote sharing & functional economy
A city can support sharing initiatives originated by citizens by providing a space or people to help in the organization, but they can also share their own assets as cars, tools, or buildings. In close partnership with ESPON, the partnership for Circualr economy has created a Collaborative Economy Knowledge Pack for cities.
![]() Raise awareness and coach citizens
Raise awareness and coach citizens
Cities who invest in awareness-raising and training of citizens, see an increase of bottom-up initiatives and a wider acceptance of necessary actions. The Urban Resource Centres described in the Urban Agenda are testbeds for circular solutions and influence the behaviour of citizens.(link to pdf?) Examples of collaboration with schools and Higher Education can also be found on the #CEstakeholderEU.
![]() Support bottom up initiatives through legislation, funding, cooperation, communication,...
Support bottom up initiatives through legislation, funding, cooperation, communication,...
When citizens organise events, repair cafes, and circular challenges, a city can help with the communication, promotion and with the exchange of knowledge and experiences. But, as a city you can also offer support with financial incentives. More information in the Circular City Funding Guide.
Stimulate Entrepreneurs & Innovation
![]() Stimulate local symbioses through (business park) networks, smart technologies,...
Stimulate local symbioses through (business park) networks, smart technologies,...
Cities play a crucial role in local symbioses because they have the overview of resources and stakeholders in their region. The Circular Resource Management Roadmap created within the Urban Agenda Circular Economy Partnership helps cities to create a step by step resource efficiency plan.
![]() Create incentives to attract circular business (offer space, taxes, subsidies,...)
Create incentives to attract circular business (offer space, taxes, subsidies,...)
Cities can support businesses by simplifying legislation, or adjusting the city tax system in favoure of circular business models. Examples on financial support can be found in the Circular City Funding Guide.
Startups or companies who invest in circular business models need extra marketing support to inform potential clients. Cities have a lot of communication tools to give those companies extra exposure, while a city also benefits from this publicity. Success stories can be posted and found on the #CEstakeholderEU.
Circular strategies to focus on
GENERAL AND TECHNICAL NUTRIENTS – The 9 R's









BIOLOGICAL NUTRIENTS





Bring clarity in complexity: make your own sheets
The overview sheet can be downloaded freely. You can use it as a tool to show the city governance model behind a certain circular case: who took the initiative, which new partnerships were forged, and what results did this lead to?
In that way, the cases transcend the facts & figures, telling the story behind the project. Give it a try, and don’t hesitate to share your experiences.
Governance sheets from European cities
Check out our other inspiring infographics
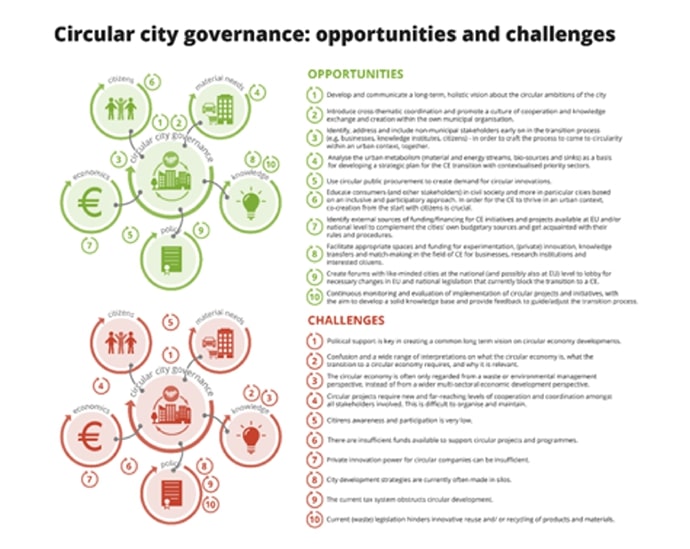
Circular city governance: opportunities and challenges
Overview based on interviews with the European frontrunners
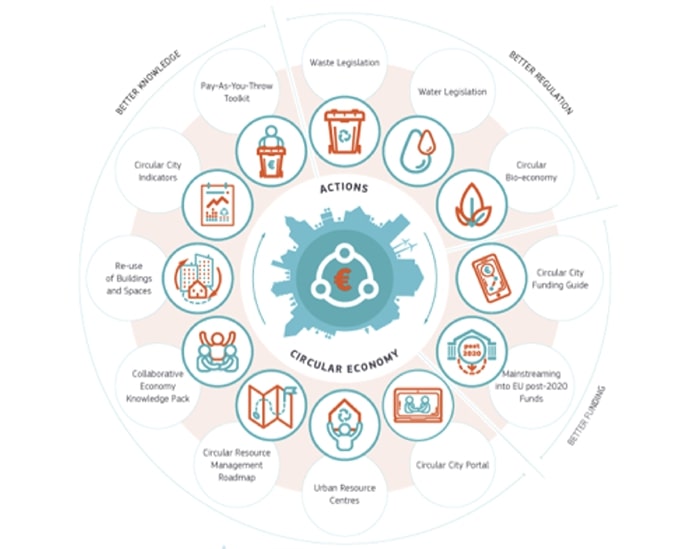
Circular city governance: actions
All 12 actions on which partnership worked on
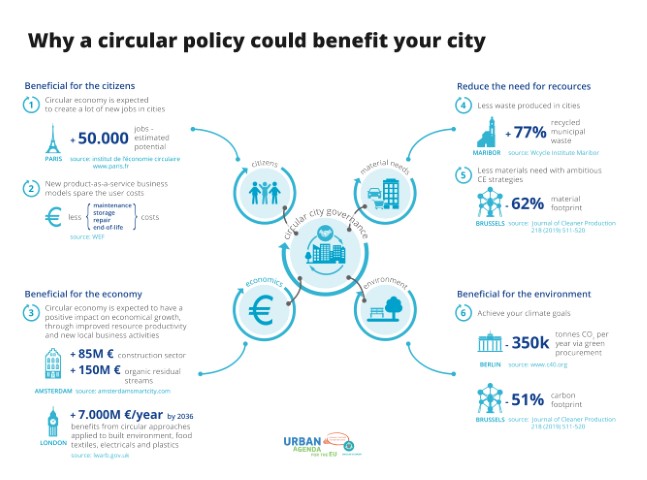
Why a circular governance could benefit your city
Investing in CE has many benefits for cities
Interesting networks and platforms for circular cities

EU Circular Economy Stakeholder Platform
A joint initiative by the European Commission (EC) and the European Economic and Social Committee (EESC) to exchange cases and strategies. The governance sheets from the Urban Agenda are uploaded here.

Circular City Funding Guide
This guide provides users with information on the circular economy in the urban context and enable them to navigate through the broad and diverse funding landscape. It also gives guidelines to develop circular funding programmes.

Urban Agenda Circular Economy
A partnership of cities, member states, networks and EC worked on 12 actions on better knowledge, better legislation and better funding in which cities could have an impact to reach the Circular Economy goals.
European Commission OneStopShop
This page provides information on EU policies such as climate change adaptation, mobility or circular economy that directly impact cities and urban areas.

Local & Regional Europe
The Council of European Municipalities and Regions (CEMR) represents the interests of Europe's local and regional governments and their associations in more than 40 countries. Circular economy being one of the key activities.

Eurocities
Network of major European cities, supporting the transition to a circular economy as part of a prosperous local economy.

Circular Europe
Network A gateway to best practices on circular economy and resource efficiency from cities and regions.

C40 cities Network of the world’s megacities committed to addressing climate change. C40 supports cities to collaborate effectively, share knowledge and drive action on climate change with a network dedicated on ‘waste to resources’. To the website >

OECD The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, transitioning to a circular economy is key for a prosperous, inclusive and sustainable future. To the website >
Ellen McArthur Foundation
Works to inspire a generation to re-think, re-design and build a positive future circular economy.

Reburg
What would life look like in a circular economy? What would businesses do? What kind of spaces would we use to live, work and play? To explore these questions we have designed the city of Reburg, where the circular economy comes to life.

Urban Data platform Plus
Provides access to information on the status and trends of cities and regions and to EU supported urban and territorial development strategies.